Catalytic Converters
For a cars internal combustion engine to operate, a controlled combustion reaction needs to occur inside the vehicle’s engine. But this reaction also produces harmful burnt gases that contribute significantly to air pollution. And good air quality is very important for an individual’s overall health.
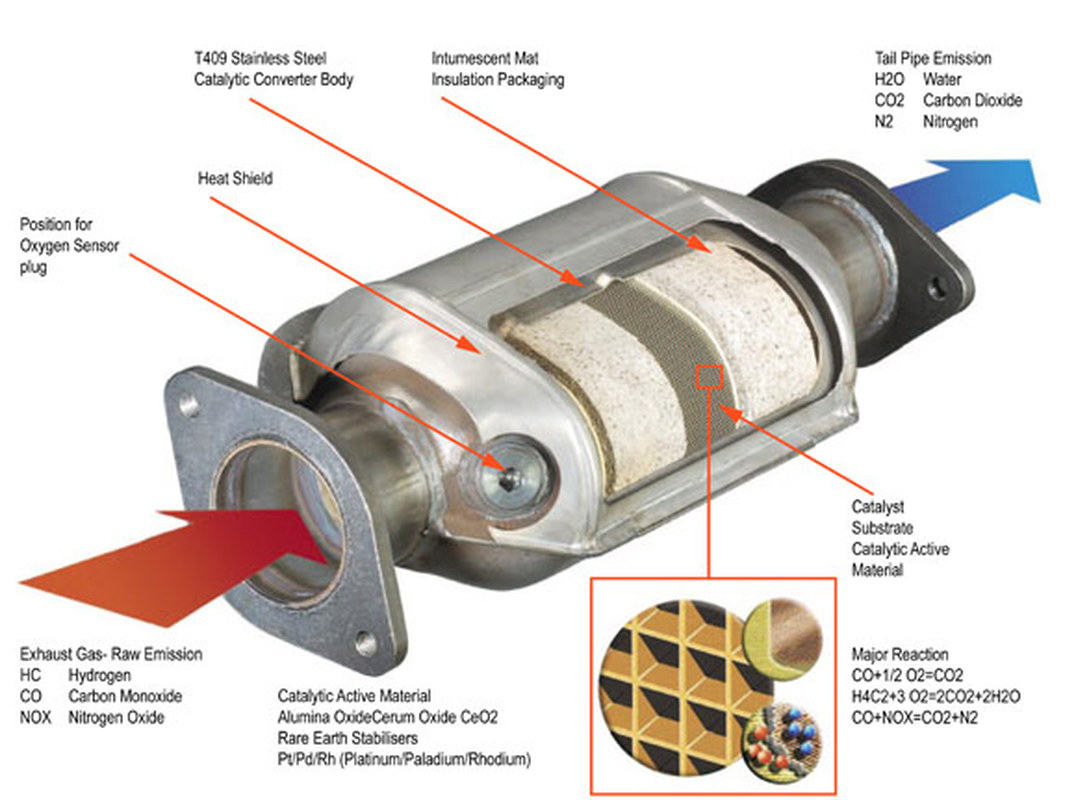
In order to reduce air pollution, modern vehicles are equipped with a device called a catalytic converter that reduces emissions of three harmful compounds found in car exhaust:
Carbon monoxide (a poisonous gas)
Nitrogen oxides (a cause of smog and acid rain)
Hydrocarbons (a cause of smog)
These are converted into less harmful compounds before leaving the car’s exhaust system. This is accomplished using a catalyst, which gives the device its name.
The catalyst used in a catalytic converter is a combination of platinum (Pt), palladium (Pd), and rhodium (Rh). These metals coat a ceramic honeycomb (or ceramic beads) contained within a metal casing that is attached to the exhaust pipe. The catalytic converter’s honeycomb structure provides the maximum surface area on which reactions can take place while using the least amount of catalyst.
A reduction and oxidation reaction occurs inside the device. Carbon monoxide (CO) in converted to carbon dioxide (CO2). Nitrogen oxides (NOx) are broken down into nitrogen gas (N2) and oxygen gas (O2). And hydrocarbons (HC) are converted into carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O).
Now here’s the slightly complicated bit:
First of all, the catalytic converter uses a reduction catalyst composed of platinum and rhodium to reduce the nitrous oxides. As the nitrous oxide molecules (NO and NO2) pass through the device, the catalyst removes the nitrogen atom, allowing the free oxygen to form oxygen gas (O2). The nitrogen atom that is attached to the catalyst reacts with other attached nitrogen atoms to form nitrogen gas (N2).
Reduction Reaction 1: 2NO => N2 + O2
Reduction Reaction 2: 2NO2 => N2 + 2O2
In the second stage of the reaction, an oxidative catalyst of platinum and palladium decreases emissions of carbon monoxide (CO) and unburned hydrocarbons (HC).
Oxidation Reaction 1: 2CO + O2 => 2CO2
Oxidation Reaction 2: H4C2 + 3O2 => 2CO2 + 2H2O
Reducing Pollution
In petrol engines, catalytic converters are reliable and efficient at reducing pollution. They convert an estimated 90% of the hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen oxides produced into less harmful compounds. But they do not reduce harmful emissions of carbon dioxide (CO2), which is a greenhouse gas that contributes significantly to global warming.
However, catalytic converters are less efficient when used with diesel engines, which run colder than gasoline engines. Catalytic converters work best at higher temperatures. Diesel engines also produce particles such as soot. But adding a diesel particulate filter (DPF) to the catalysts in the catalytic converter can reduce emissions of ultra-fine particles by up to 99%.




























































